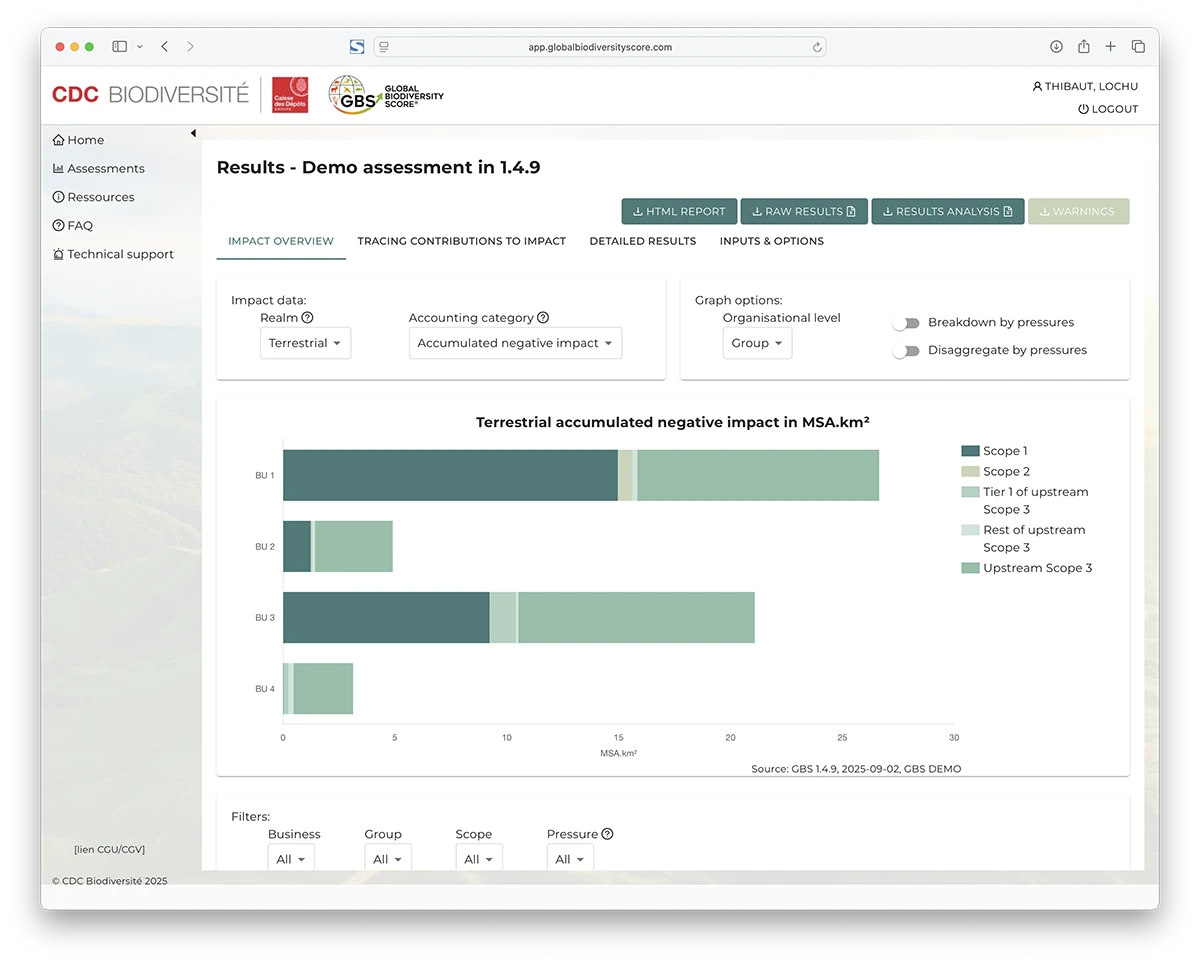
In an era of accelerating biodiversity loss, businesses are under growing pressure to understand and reduce their environmental impacts, not only for regulatory compliance but also to secure their economic models, limit their risk exposure and contribute to a nature-positive future. The Global Biodiversity Score (GBS) is a scientifically grounded, quantitative tool developed by CDC Biodiversité for assessing the biodiversity footprint and ecosystem dependencies of companies across their value chains.
With the GBS, companies can: